Carat Weight
Carat weight is simply the weight of the diamond.
The following units of weight are used:
- 1 carat (ct) is equivalent to 1/5 gram
- 1 point is equivalent to 1/100 or .01 ct
Carat weight alone does not indicate anything regarding the proportions of a diamond. Therefore, carat weight alone has nothing to do with its beauty, brilliance or size when viewing the diamond face up.
Carat weight relates to value simply because larger diamonds are rare and therefore, more valuable. This is why, for example, a three carat diamond is much more valuable than three one carat diamonds.
Color
Diamond is carbon, crystallized at high temperatures and pressures deep within the earth. In its pure form, diamond is essentially colorless. Color occurs in diamond when minute amounts of a trace element such as nitrogen enter the crystal structure, or the structure itself undergoes a slight misalignment. (It takes as little as 1 part nitrogen in 10,000 parts carbon to produce a bright yellow color in diamond).
A diamond should be graded for color before it is set by comparing it to a set of master diamonds under specific lighting conditions. Once the diamond is set, the color can be affected by the style and color of the mounting.
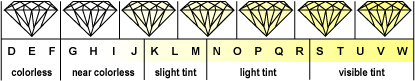
The most widely used grading scale for color was developed by GIA and uses a scale that ranges from D to Z.
| D |
Absolutely colorless
|
Diamonds in this color grade are extremely rare. |
|
|
||
| E-F |
Color-less
|
Diamonds in this range are considered to be colorless, although minute traces of color may be detectable by an expert under controlled grading conditions. |
|
|
||
| G-H |
Near color-less
|
Diamonds in this range will “face up” colorless, i.e. slight traces of color will not be apparent in mounted stones to other than the trained eye. Color may be observed when compared loose to diamonds of higher color grades. |
|
|
||
| I-J |
Near color-less
|
Color is slightly detectible in this range, but these grades offer an excellent value. |
|
|
||
| K-M |
Slight tint
|
Color is noticeable in this range, although a well-cut round brilliant will visibly display less color than most fancy cuts. |
|
|
||
| N-Z |
Tinted
|
Diamonds in this range will display obvious color. |
|
|
||
Fancy colored diamonds of yellow, brown, pink, blue, etc. are graded on a different scale than the D – Z described above.
Clarity
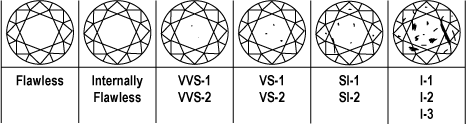
Clarity is the description of the internal characteristics or inclusions in a diamond. While diamonds that are flawless are rare and most valuable, the wearer will see no difference between a flawless diamond and a diamond with SI-1 clarity without magnification. Clarity is generally described by the following scale:
| Flawless | Free from all inclusions or blemishes at 10x magnification |
|
|
|
| Internally Flawless |
No inclusions visible at 10x; insignificant surface blemishes only |
|
|
|
| VVS-1 VVS-2 |
Minute inclusions – extremely difficult to see at 10x Minute inclusions – very difficult to see at 10x |
|
|
|
| VS-1 VS-2 |
Minor inclusions – difficult to see face-up at 10x Minor inclusions – somewhat easy to see face-up at 10x |
|
|
|
| SI-1
|
Noticeable inclusions – easy to see at 10x- not visible to the unaided eye |
| SI-2 | Noticeable inclusions – very easy to see at 10X, may be faintly visible in the face up position or noticeable through the pavilion to the unaided eye |
|
|
|
| I-1 I-2 I-3 |
Obvious inclusions at 10x – visible to the unaided eye Obvious inclusions – easily visible to the unaided eye Prominent inclusions – extremely easy to see with the unaided eye; usually affect durability |
|
|
|
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the luminescent effect produced by some diamonds when exposed to long-wave ultraviolet light (black lights in nightclubs). Approximately 60% of all diamonds fluoresce, typically blue in color and the intensity varies. The GIA and AGS labs describe the visible effects of fluorescence using grades of negligible, inert, faint, medium, strong or very strong.
You will not see fluorescence in the range from negligible to medium under ordinary conditions. The grades of strong and very strong may make a colorless diamond appear bluish or make a diamond with a faint tint of yellow appear whiter, while occasionally giving the diamond a hazy or oily effect. Diamonds with strong and very strong fluorescence are usually priced lower than other diamonds.
